Once the stuff of science fiction, digital twins have rapidly evolved into one of the most practical and transformative technologies in modern business. These dynamic virtual replicas of physical systems are no longer confined to aerospace labs or high-tech manufacturing floors—they’re now reshaping entire industries.
For many organizations, it’s not just about innovation—it’s about result. Digital twins promise measurable returns: reduced downtime, faster development cycles, smarter decision-making, and even new revenue streams. Yet, like any emerging technology, their success depends on thoughtful implementation.
In this article, we’ll explore the real-world practicality of digital twins, the industries leading their adoption, the benefits they unlock, and how to evaluate their return on investment.
Whether you’re a strategist, technologist, or simply curious about the future of digital operations, this piece will help you understand the how and why behind digital twins.
Watch Impact’s webinar, Why Your Tech Rollouts Fail (and What to Do About It), to learn how to properly onboard new technology straight from the experts.
What Is a Digital Twin?
A digital twin is a dynamic, virtual representation of a physical object, system, or process. Unlike a static model or simulation, a digital twin is continuously updated with real-time data from its physical counterpart, allowing it to mirror behavior, predict outcomes, and optimize performance across its lifecycle.
The concept originated in aerospace. NASA used early forms of digital twins to simulate spacecraft behavior during the Apollo missions, but it has since evolved into a foundational technology across industries like manufacturing, healthcare, energy, and smart infrastructure.
At its core, a digital twin consists of three key components:
- The physical entity (e.g., a machine, building, or process).
- The digital replica, which models the entity’s structure and behavior.
- The data connection, often referred to as the “digital thread,” which enables real-time synchronization between the two.
This real-time feedback loop allows organizations to simulate scenarios, test changes without risk, and make data-driven decisions. For example, a manufacturer might use a digital twin of a production line to identify bottlenecks before they occur, while a city planner could simulate traffic flow using a digital twin of an urban district.
As AI and IoT technologies mature, digital twins are becoming more accessible and powerful while also being easier to build and more capable of simulating complex behaviors under any number of conditions.
Industries Adopting Digital Twins
Digital twins are no longer confined to R&D labs or futuristic tech demos; they’re actively transforming how entire industries operate.
By creating real-time, data-driven virtual replicas of physical systems, digital twins enable organizations to simulate, monitor, and optimize performance with unprecedented precision.
Here’s a look at the industries leading the charge and what’s driving adoption:
1. Manufacturing: The Pioneer of Digital Twin Adoption
Manufacturing remains the most mature sector in digital twin deployment. From simulating production lines to monitoring equipment health, manufacturers use digital twins to:
- Predict maintenance needs and prevent costly downtime.
- Optimize workflows and reduce waste.
- Accelerate product development through virtual prototyping.
Smart factories are leveraging digital twins to create closed-loop systems where real-time data informs continuous improvement.
2. Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Outcomes
In healthcare, digital twins are being used to model everything from hospital operations to individual patient physiology. Applications include:
- Personalized treatment planning using patient-specific models.
- Simulating surgical procedures before they’re performed.
- Managing hospital resources and patient flow more efficiently.
This data-driven approach is helping providers improve outcomes while reducing costs.
3. Energy and Utilities: Monitoring Complex Systems
Energy companies use digital twins to manage infrastructure such as power grids, wind farms, and oil rigs. Benefits include:
- Real-time monitoring of asset performance.
- Predictive analytics for maintenance and safety.
- Simulation of energy demand and supply scenarios.
These capabilities are critical for ensuring reliability and sustainability in a rapidly evolving energy landscape.
4. Smart Cities and Infrastructure: Building Resilience
Urban planners and civil engineers are adopting digital twins to design and manage smart cities. Use cases include:
- Simulating traffic flow and public transportation systems.
- Monitoring structural health of bridges and buildings.
- Planning for disaster response and climate resilience.
Digital twins help cities become more adaptive, efficient, and human-centric.
5. Logistics and Supply Chain: Improving Agility
In logistics, digital twins offer a real-time view of supply chain operations. They’re used to:
- Track shipments and inventory across global networks.
- Simulate disruptions and test contingency plans.
- Optimize warehouse layouts and delivery routes.
This visibility enables faster, more informed decision-making in a volatile global market.
Key Benefits of Implementing Digital Twins
Digital twins offer a powerful blend of real-time data, simulation, and analytics that can transform how organizations operate. One of the most immediate advantages is predictive maintenance.
By continuously monitoring equipment and systems, digital twins can detect anomalies and forecast failures before they happen, helping to avoid costly downtime.
They also enhance operational efficiency by allowing businesses to simulate and optimize processes in a virtual environment, making it easier to identify inefficiencies and test improvements without disrupting real-world operations.
In product development, digital twins accelerate innovation by enabling rapid prototyping and iterative testing. Teams can model performance, stress-test components, and refine designs virtually, which shortens development cycles and reduces R&D costs.
These virtual models also support better decision-making by allowing leaders to simulate “what-if” scenarios and assess the impact of different strategies based on real-time data.
Beyond internal operations, digital twins can improve customer experiences. In healthcare, for example, they’re used to personalize treatment plans by modeling individual patient physiology. In retail, they help optimize store layouts and inventory based on shopper behavior.
They also contribute to sustainability goals by enabling organizations to monitor energy usage, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation, especially in smart buildings and cities.
Ultimately, digital twins provide a competitive edge by laying the groundwork for integrating AI, IoT, and machine learning into core operations. This positions organizations to be more adaptive, innovative, and resilient in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Measuring the ROI of Digital Twins
While the concept of digital twins is compelling, it often comes down to a question of the ROI. Unfortunately, there’s no universal answer here, as it depends largely on the way digital twins are implemented.
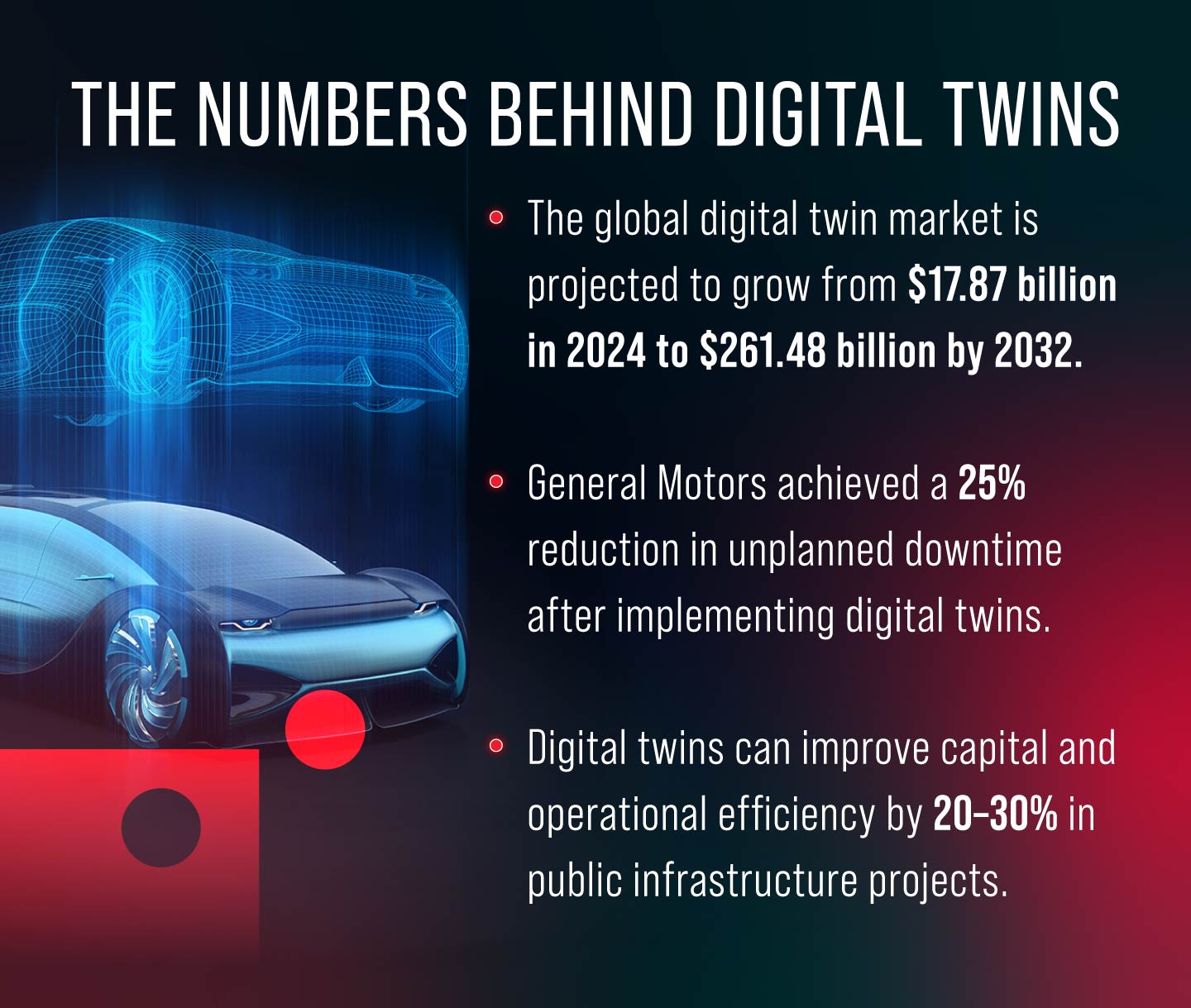
Digital twins deliver ROI by improving operational efficiency, reducing downtime, and enabling smarter decision-making. For example, companies that have adopted digital twins report measurable gains in productivity and up to a 30% reduction in operating expenses.
These savings often stem from predictive maintenance, which helps prevent costly equipment failures, and from process optimization, which reduces waste and accelerates time to market.
The ROI equation also includes intangible benefits. Digital twins enhance product quality, improve customer satisfaction, and support sustainability initiatives by optimizing resource use. In sectors like manufacturing, energy, and infrastructure, they enable scenario planning and real-time monitoring that lead to faster, more informed decisions.
However, realizing these benefits requires upfront investment in sensors, data infrastructure, and skilled personnel. That’s why a clear implementation strategy is essential.
Organizations that define specific use cases, such as reducing maintenance costs or improving asset utilization, are better positioned to track ROI and scale their digital twin initiatives effectively.
Ultimately, the ROI of digital twins isn’t just about cost savings; it’s about unlocking new value streams. Whether it’s extending the life of physical assets, accelerating innovation, or enhancing customer experiences, digital twins offer a forward-looking approach to business performance that pays dividends over time
Challenges to Consider Prior to Adoption
Despite their promise, digital twins come with real-world complexities that organizations must address before diving in. One of the biggest hurdles is integrating data from disparate systems. Digital twins rely on continuous, high-quality data streams, but many companies still operate with siloed or outdated infrastructure.
Security and privacy are also critical concerns. Because digital twins often process sensitive operational and customer data, they introduce new vulnerabilities. Without strong cybersecurity protocols and compliance frameworks, organizations risk exposing themselves to breaches or regulatory issues.
Cost is another factor. Building and maintaining a digital twin requires investment in sensors, connectivity, modeling tools, and skilled talent. For companies without a clear use case or roadmap, the risk of overbuilding or underutilizing the technology is high.
Finally, not every asset or process needs a digital twin. Starting with a focused, high-impact use case helps validate the value and build momentum for broader deployment. A thoughtful, phased approach is key to avoiding wasted effort and maximizing return.
Final Thoughts on Using Digital Twins
From manufacturing lines to hospital systems, from energy grids to urban infrastructure, the ability to simulate, monitor, and optimize in real time is unlocking new levels of efficiency and insight.
But the value of digital twins isn’t just in the technology—it’s in the strategy. Organizations that approach adoption with clear goals, strong data foundations, and a willingness to evolve their processes are the ones seeing the greatest returns.
As digital ecosystems grow more complex and interconnected, digital twins offer a way to bring clarity, control, and foresight to the physical world.
Get expert advice on how to effectively onboard new technology in Impact’s webinar, Why Your Tech Rollouts Fail (and What to Do About It).